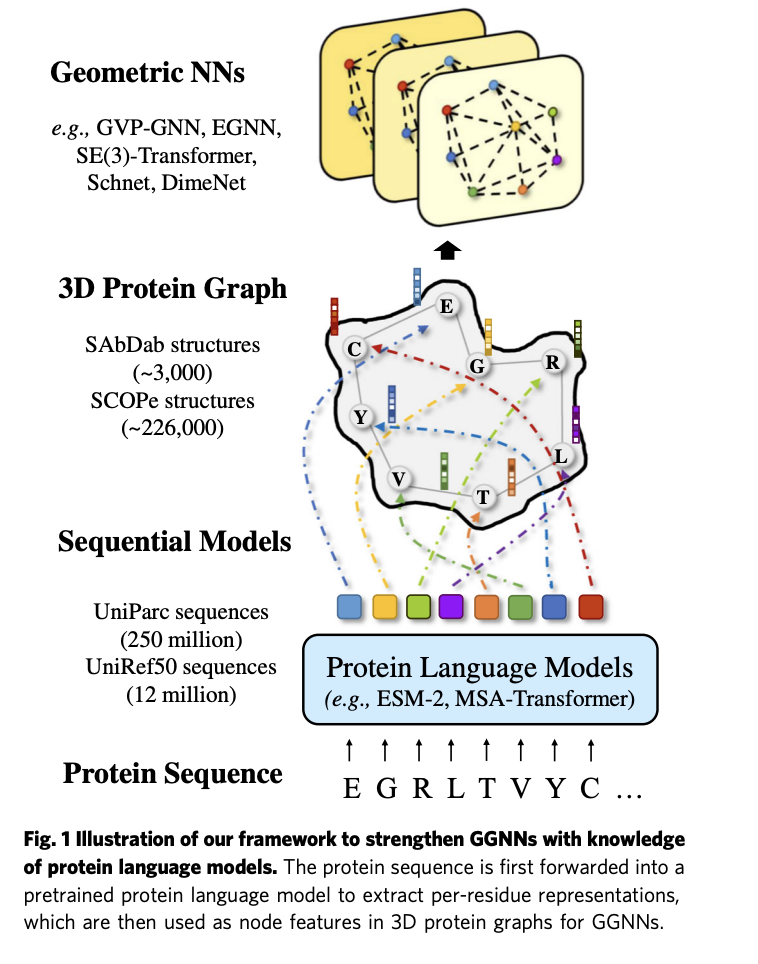
Researchers at Stanford Present A Novel Artificial Intelligence Method that can Effectively and Efficiently Decompose Shading into a Tree-Structured Representation
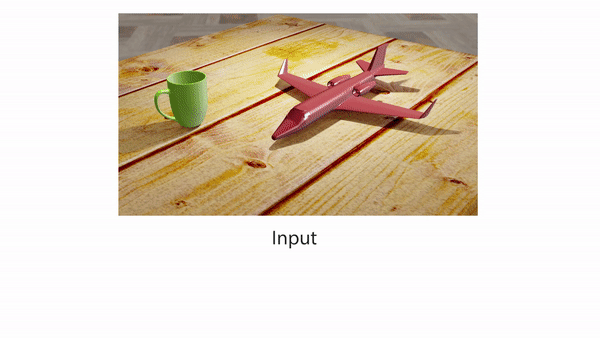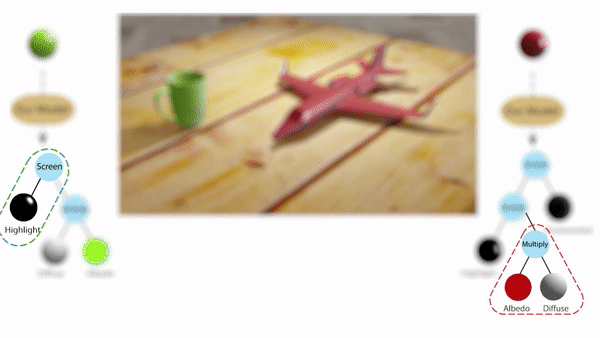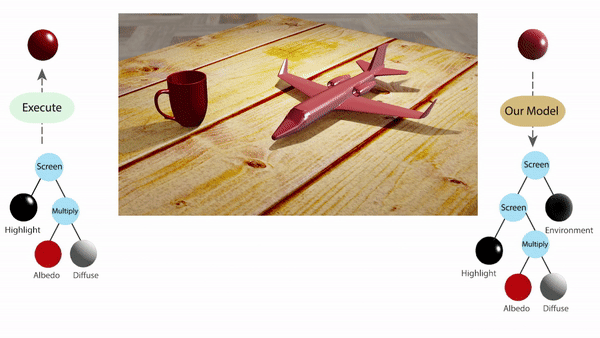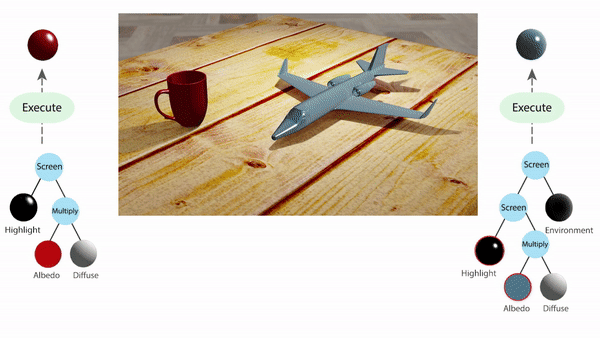
In computer vision, inferring detailed object shading from a single image has long been challenging. Prior approaches often rely on complex parametric or measured representations, making shading editing daunting. Researchers from Stanford University introduce a solution that utilizes shade tree representations, combining basic shading nodes and compositing methods to break down object surface shading…